At Ori, one of our goals is to provide more compute choices because every AI workload has its unique needs. As demand for AI inference grows, NVIDIA L40S GPU has become a popular choice to serve small to medium sized AI models. This article will help you understand if L40S is the right choice for your workload and how you can deploy this powerful GPU on Ori Global Cloud.
A versatile GPU that excels at many tasks
Powered by the flexible Ada Lovelace architecture that includes both 4th Gen Tensor Cores and 3rd Gen ray tracing (RT) cores, the L40S is one of the most versatile GPUs in the NVIDIA lineup. While the Tensor cores and Deep Learning Super Sampling (DLSS) help deliver strong AI and data science performance, the RT cores enable photorealistic rendering, enhanced ray tracing, and powerful shading makes this data center GPU also suitable for professional visualization workloads.
Here’s a snapshot of the NVIDIA L40S specifications:
| NVIDIA L40S GPU Specs |
|
GPU Architecture
|
NVIDIA Ada Lovelace
|
|
GPU Memory
|
48GB GDDR6 with ECC
|
|
Memory Bandwidth
|
864GB/s
|
|
Interconnect Interface
|
PCIe Gen4 x16: 64GB/s bidirectional
|
|
NVIDIA Ada Lovelace CUDA® Cores
|
18,176
|
|
NVIDIA Third-Generation RT Cores
|
142
|
|
NVIDIA 4th Gen Tensor Cores
|
568
|
|
NVIDIA® NVLink® Support
|
No
|
Consider NVIDIA L40S for these use cases
Affordable AI inference, especially for small and medium sized LLMs, and multimodal models, with L40S GPUs being 28% and 40% cheaper than A100 and H100 PCIe respectively. Here are some examples of multimodal models (Llama 3.2 11B Vision, Flux Schnell) that run smoothly on L40S GPUs.
- Train or finetune small AI models, where L40S delivers strong computational power without the need for extensive capabilities of heavyweight GPUs like H100.
- Perfect for graphics-intensive applications requiring advanced rendering and real-time processing. Equipped with 3rd Gen RT Cores, that deliver up to twice the real-time ray-tracing performance of the previous generation, the L40S GPU from NVIDIA enables breathtaking visual content and high-fidelity creative workflows, from interactive rendering to real-time virtual production.
- A versatile mix of visual and general-purpose computing makes it perfect for a wide range of uses, like product engineering, architecture, construction, virtual reality (VR), and augmented reality (AR).
- When you need strong performance but don’t require multiple GPUs for large parallel tasks. The L40S features higher onboard memory (48 GB) than several NVIDIA GPUs such as V100, V100S, and L4, making it capable of handling comparatively larger models.
NVIDIA H100 vs L40s specifications
| |
L40S |
H100 SXM |
H100 PCIe |
|
GPU architecture
|
Ada Lovelace
|
Hopper
|
|
Use cases
|
AI inference, 3D graphics, rendering, video processing, engineering, architecture, VR
|
Foundation model training, AI inference, HPC, LLMs, Multimodal models, Image & video generation, Large scale production ready models
|
|
Fractional GPU support
|
No
|
Yes
|
|
Multi-GPU support
|
No
|
Yes
|
|
GPU memory (VRAM)
|
48 GB GDDR6 with ECC
|
80 GB HBM3
|
80 GB HBM2e
|
|
Memory Bandwidth
|
864 GB/s
|
3.35 TB/s
|
2 TB/s
|
|
NVLink support
|
No
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
FP64
|
Not supported
|
33.5 TFLOPS
|
25.6 TFLOPS
|
|
FP64 Tensor Core
|
Not supported
|
66.9 TFLOPS
|
51.2 TFLOPS
|
|
FP32
|
91.6 TFLOPS
|
66.9 TFLOPS
|
51.2 TFLOPS
|
|
FP16
|
Not available
|
133.8 TFLOPS
|
102.4 TFLOPS
|
|
BF16
|
Not available
|
133.8 TFLOPS
|
102.4 TFLOPS
|
|
TF32 Tensor Core
|
183 TFLOPS I 366 TFLOPS*
|
494.7 TFLOPS | 989.4 TFLOPS*
|
378 TFLOPS | 756 TFLOPS*
|
|
FP16 Tensor Core
|
362.05 TFLOPS I 733 TFLOPS*
|
989.4 TFLOPS | 1978.9 TFLOPS*
|
756 TFLOPS | 1513 TFLOPS*
|
|
BF16 Tensor Core
|
362.05 TFLOPS I 733 TFLOPS*
|
989.4 TFLOPS | 1978.9 TFLOPS*
|
756 TFLOPS | 1513 TFLOPS*
|
|
FP8 Tensor Core
|
733 TFLOPS I 1,466 TFLOPS*
|
1978.9 TFLOPS | 3957.8 TFLOPS*
|
1513 TFLOPS | 3026 TFLOPS*
|
|
INT8 Tensor Core
|
733 TOPS I 1,466TOPS*
|
1978.9 TOPS | 3957.8 TOPS*
|
1513 TOPS | 3026 TOPS*
|
*With Sparsity
AI Inference: NVIDIA L40S vs H100
Llama 2 Performance & Cost Comparison
|
Llama-2-7B **
|
L40S Throughput
|
H100 SXM High Throughput
|
L40S Cost / 1M tokens
|
H100 SXM Cost / 1M tokens
|
|
Input tokens = 128, Output tokens = 128
|
6,656 tokens/s/GPU
|
17,685 tokens/s/GPU
|
$0.082
|
$0.059
|
|
Input tokens = 128, Output tokens = 2048
|
1,592 tokens/s/GPU
|
6,815 tokens/s/GPU
|
$0.342
|
$0.155
|
|
Input tokens = 2048, Output tokens = 2048
|
653 tokens/s/GPU
|
2,820 tokens/s/GPU
|
$0.834
|
$0.374
|
**Tensor Parallelism = 1, FP8, TensorRT-LLM 0.11.0 Framework
***The performance numbers are based on benchmarks from NVIDIA. Actual performance numbers may vary depending on a variety of factors such as system configuration, form factor, operating environment, and type of workloads. We encourage users to run their own benchmarks before deciding on GPUs for more extensive workloads.
Stable Diffusion AI Performance & Cost Comparison
|
Stable Diffusion XL
|
NVIDIA L40S
|
NVIDIA H100 SXM
|
|
Images per hour*
|
1296
|
2952
|
|
Ori Global Cloud Pricing
|
$1.96/hr
|
$3.8/hr
|
|
Latency per image
|
2812.19 ms
|
1213.17 ms
|
|
Cost of 1000 images**
|
$1.512
|
$1.287
|
**The performance numbers are based on benchmarks from NVIDIA. Actual performance numbers may vary depending on a variety of factors such as system configuration, form factor, operating environment, and type of workloads. We encourage users to run their own benchmarks before deciding on GPUs for more extensive workloads.
Although H100 SXM GPU’s per hour cost is higher than the NVIDIA L40S price, it is cost-effective when running inference at large-scale, using multi-GPU configurations or training large models. On the other hand, the L40S is more affordable for smaller inference tasks and works well when you only need a single GPU.
The L40S’ flexibility enables it to run generative AI inference ranging from LLMs to image generation, and multimodal models. It is also a better fit for video editing, graphics rendering and traditional content processing workloads. NVIDIA L40S is also a great choice for AI experimentation and when you don’t need maximum GPU utilization.
How does NVIDIA L40S compare with NVIDIA A100
Although both of these GPUs are a fantastic choice for inference, the A100 GPU can also double as a training-ready GPU for deep learning and HPC workloads. A100’s superior memory specifications and support for multiple GPUs, gives it more range. A100 GPUs also support fractional instances, making them equally flexible for smaller workloads.
Here’s a quick rundown of A100 vs L40S specifications
| |
L40S
|
A100 PCIe
|
|
GPU architecture
|
Ada Lovelace
|
Ampere
|
|
Use cases
|
AI inference, 3D graphics, rendering, video processing
|
AI Training, AI inference, HPC / Scientific computing
|
|
Fractional GPU support
|
No
|
Yes
|
|
Multi-GPU support
|
No
|
Yes
|
|
GPU memory (VRAM)
|
48GB GDDR6 memory with ECC
|
80 GB HBM2e
|
|
Memory Bandwidth
|
864GB/s
|
1,935GB/s
|
|
NVLink support
|
No
|
Yes
|
|
FP64, FP64 Tensor Core support
|
No
|
Yes
|
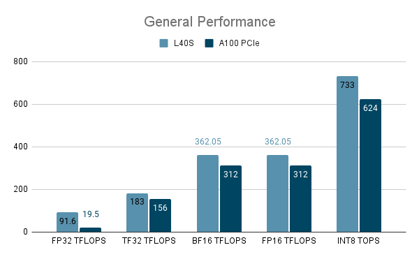
In terms of sheer performance, L40S has an edge with up to 4.7x (FP32 TFLOPS) higher performance. However, for many workloads GPU memory (VRAM) is as important as the processing power, especially as models grow larger in terms of parameters, where A100 shines with its larger onboard memory.
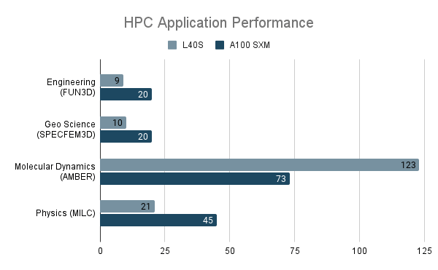
The NVIDIA A100, with its support for 64-bit formats, strong fp64 performance and larger memory capacity outperforms the L40S for HPC workloads.
Get started with NVIDIA L40S today
The NVIDIA L40S GPU offers a versatile balance of AI inference performance and 3D rendering capabilities, making it ideal for small to medium AI models, graphics-heavy applications, and multimodal models. It is a cost-effective alternative to the H100 and A100 GPUs for smaller inference tasks, while being well-suited for AI and content creation workloads.
Deploy NVIDIA L40S on Ori Global Cloud in any of these modes:
-
GPU instances, on-demand virtual machines backed by top-tier GPUs to train, finetune and serve AI models.
-
